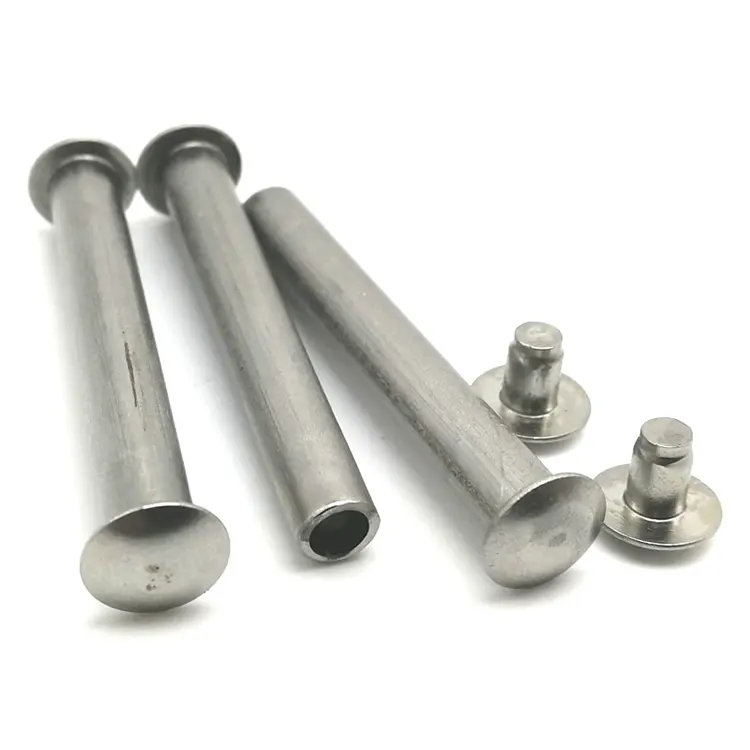
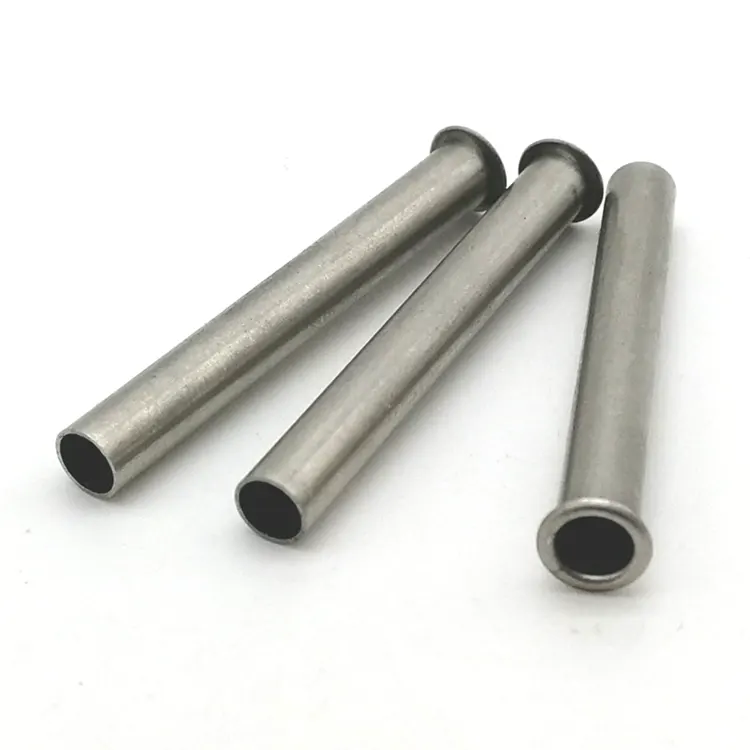
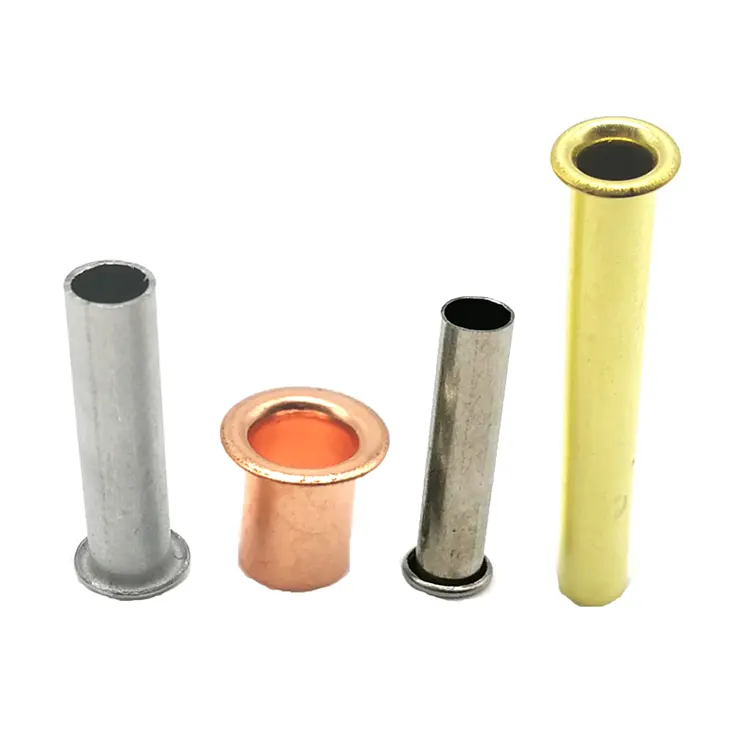
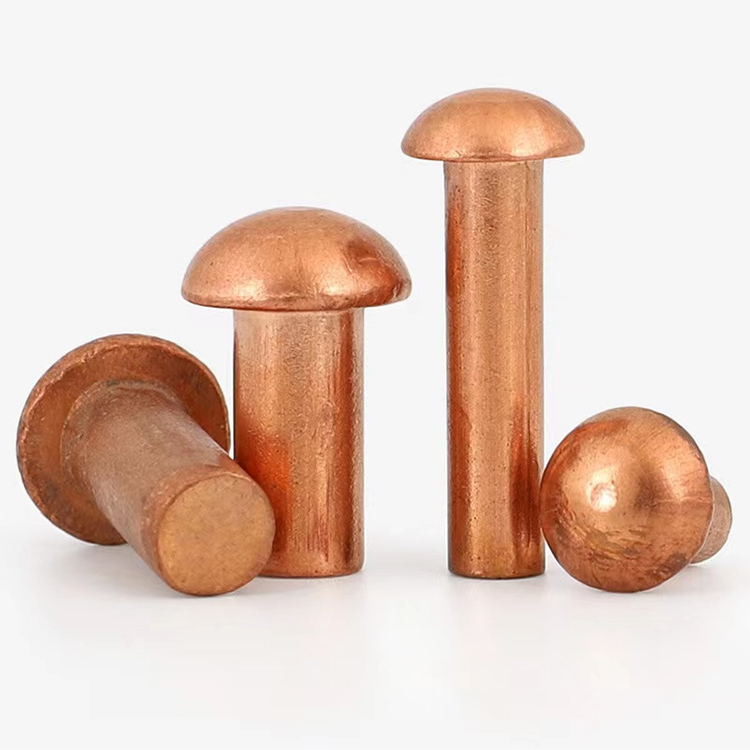
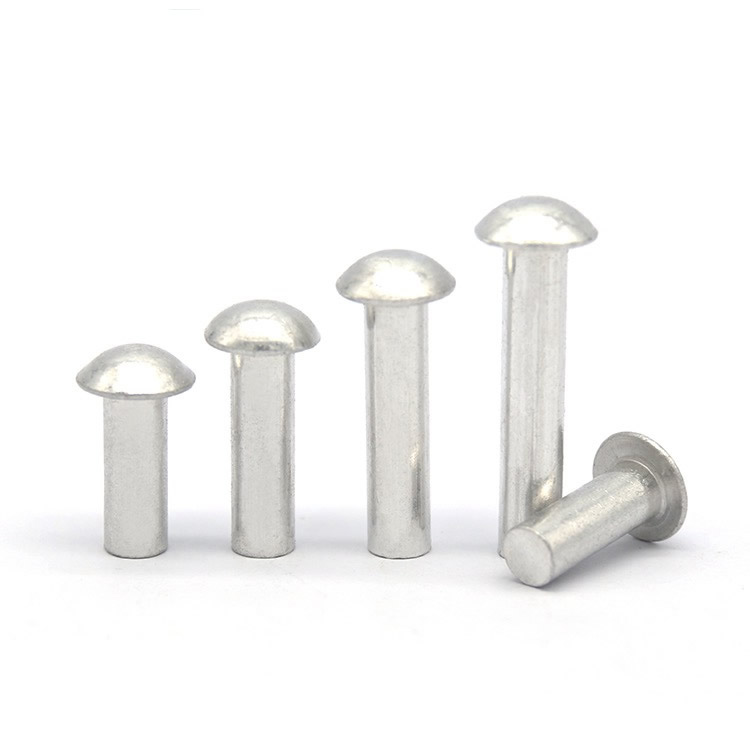
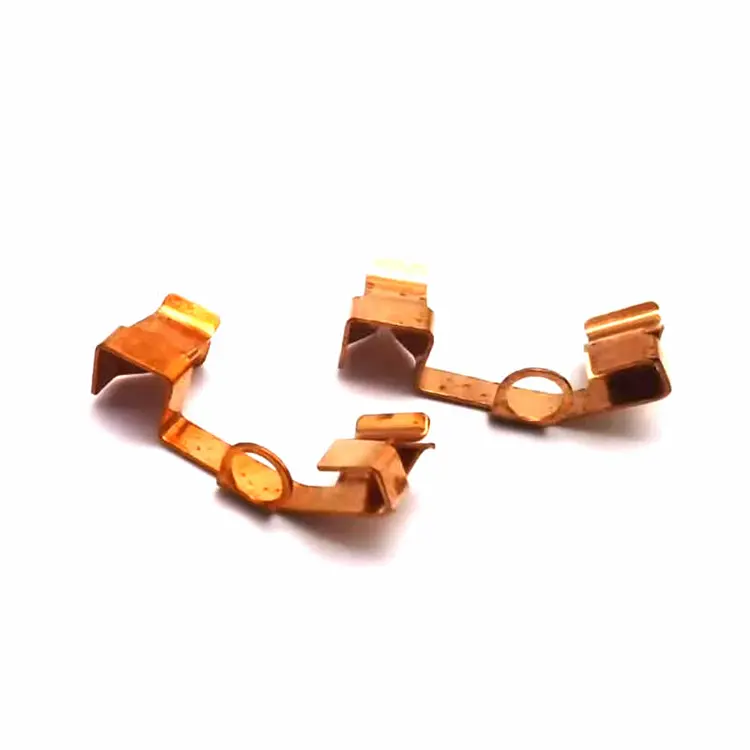
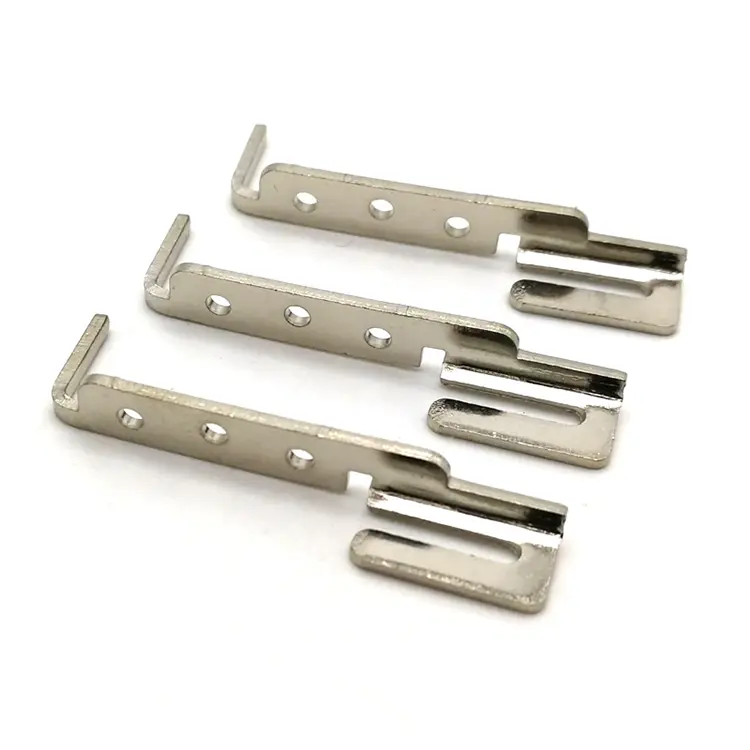
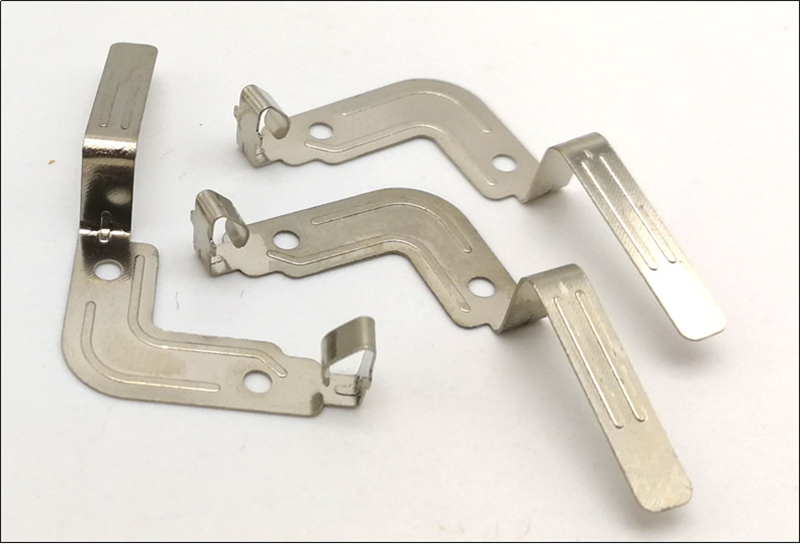
Parti di timbratura
Notin invites you to visit our factory to purchase the newest, best-selling, affordable, and high-quality Stamping Parts. We are looking forward to working with you.
What are stamping parts?
stamping parts are metal parts manufactured through a stamping process, using dies and presses to shear, bend, and stretch sheet metal (such as steel, aluminum, or copper) to form the desired shape. The core characteristics of this process are high efficiency and precision. Stamping can be categorized into two main types: separation processes (such as punching and blanking) and forming processes (such as drawing and flanging), to meet different structural requirements.
What are the main characteristics of stamping parts?
1. Compared to casting and forging, stamping parts are thinner, more uniform, lighter, and stronger. Stamping can produce workpieces with ribs, ribs, corrugations, or flanging that are difficult to create using other methods to increase rigidity.
2. Due to the use of dies, workpiece precision can reach micron levels, with high repeatability and consistent specifications, including punched holes and bosses. Cold stamped parts generally require no or minimal cutting.
3. The precision and surface finish of hot stamped parts are lower than those of cold stamped parts, but still superior to those of castings and forgings, requiring less cutting. 4. Using composite dies, particularly multi-station progressive dies, allows multiple stamping steps to be completed on a single press, achieving automated production from strip uncoiling, leveling, blanking, to forming and finishing.
5. High production efficiency, good working conditions, and low production costs enable the production of hundreds of pieces per minute. Stamping is primarily categorized by process into separating and forming.
6. The surface and internal properties of the stamped sheet material significantly impact the quality of the stamped product, requiring consistent thickness and uniformity of the stamped material.
7. The surface must be smooth, free of scars, scratches, or surface cracks, with uniform yield strength and no apparent directional variation; high uniform elongation; low yield strength; and low work hardening.
Metal Stamping Design Process
Metal stamping is a complex process that may include numerous metal forming steps—blank-cutting, punching, bending, and piercing, among others. Blanking: This process involves cutting the rough outline or shape of the product. This stage is focused on minimizing and avoiding burrs, which increase part cost and extend delivery time. This step is where you determine the hole diameter, geometry/taper, edge-to-hole spacing, and insert the first punch.
Bends: When designing bends in stamped metal parts, it's important to leave enough material—make sure to design your part and its blank so there's enough material to make the bend. Some important factors to keep in mind:
If the bend is too close to the hole, it may deform.
Notches, tabs, and notches should be designed with a width of at least 1.5 times the material thickness. Any smaller and they may become difficult to manufacture due to the forces exerted on the punch, causing them to break.
Each corner in the blank design should have a radius of at least half the material thickness.
To minimize the occurrence and severity of burrs, avoid sharp corners and complex cuts whenever possible. When these factors cannot be avoided, be sure to note the burr direction in the design so that it can be accounted for during stamping.
Coining: This action involves striking the edge of a stamped metal part to flatten or break burrs. This creates a smoother edge in the coined area of the part geometry. It can also add additional strength to localized areas of the part, which can avoid secondary operations such as deburring and grinding.
- View as
Parti di timbratura per socket
Parti di timbratura per Socket è un produttore leader di parti di timbratura in metallo progressivo, le parti di stampaggio sono ampiamente utilizzate in interruttori, relè, termostati, contattori, disconnettore, controller, timer e altri apparecchi a bassa tensione.
Per saperne di piùInvia richiestaParti stampate in metallo
Nuote Metals è specializzata nella produzione di parti timbrate in metallo internamente. Abbiamo un team interno di esperti per la progettazione di strumenti e dado, costruzione, operazioni di stampa esemplari e assemblaggio. Abbiamo più 10 anni di lavoro di lavoro in Metal Stamping Technics, inviaci il tuo disegno per una quotazione veloce.
Per saperne di piùInvia richiestaParti di timbratura in metallo
Nuote Metals è un produttore di parti di timbratura in metallo leader di parti di componenti personalizzate da una varietà di materiali di base, come alluminio, ottone, acciaio inossidabile, rame di berillio, acciaio ecc. Offriamo una vasta gamma di capacità di timbratura di metallo di precisione, tra cui: blanking, piegatura, coniatura, formazione, piercing, ecc.
Per saperne di piùInvia richiestaParti metalliche di stampaggio di precisione
I metalli Nuote possono utilizzare una varietà di metalli per produrre parti metalliche di stampaggio di precisione. Tuttavia, alcuni processi e tipi di metalli funzionano meglio nel processo di stampaggio metallico di precisione o si adattano meglio a un determinato caso d'uso.
Per saperne di piùInvia richiestaStamping in metallo di precisione
Il processo di stampaggio metallico Precision utilizza macchinari dotati di stampi per trasformare la lamiera in forme personalizzate a tolleranze incredibilmente strette. Nuote Metals è un produttore professionista di parti di timbratura in metallo a Dongguan, in Cina.
Per saperne di piùInvia richiestaSome important factors to keep in mind:
Plasticity and Grain Direction – Plasticity is a measure of the permanent deformation a material undergoes when subjected to stress. Metals with greater plasticity are more susceptible to forming. Grain direction is important in high-strength materials, such as tempered metals and stainless steel. If bending occurs along a high-strength grain, cracking is more likely.
Bending Deformation/Expansion: Bending deformation causes expansion of up to 1/3 of the material thickness. This deformation/expansion becomes more severe as the material thickness increases and the bend radius decreases. Web and "mismatch" cutting: This involves making very slight indentations or protrusions in the part, typically about 0.1mm deep. This feature is not required when using composite or transfer tools, but it is essential when using progressive dies.
Advantages and Limitations of Stamping
Advantages:
- Low cost: In mass production, the cost per part can be reduced to one-third of that of a cast part;
- High consistency: Dimensional tolerances can be controlled within ±0.1mm;
- High material utilization: Through nesting optimization, the utilization rate can reach over 85%.
Limitations:
- Long mold development cycle and high initial investment, making it unsuitable for large-scale production;
- Complex three-dimensional structures (such as hollow crankshafts) require integration with other processes.
Core Application Areas of Stamping Parts
1. Automotive Industry: Accounts for over 60% of total stamping part demand, including body panels and chassis components;
2. Electronics and Electrical: For example, metal mobile phone frames and heat sinks, thicknesses can be as thin as 0.2mm;
3. Home Appliance Industry: Refrigerator panels, air conditioner housings, etc., where surface aesthetics can be enhanced through electroplating or spraying.













